Header bidding often referred to as advance bidding or pre-bidding, is a programmatic approach to selling inventory to multiple ad exchanges at once before calling their ad servers. Publishers can now increase their revenue even more through header bidding thanks to programmatic advertising.
How does Header Bidding work?
Header bidding begins with a script inserted in the header area of the publisher’s website. The script’s code kicks in as soon as the website loads and sends requests to demand partners. The highest bidder receives first priority. By allowing all bids to compete, it tries to maximize revenue for the publisher. The publisher or header bidding partner can choose the best one, or it can transmit all of the bids to the ad server, which will choose the best in real-time and in conjunction with direct demand and other relevant line items.
For Publishers and Advertisers
For a publisher, the most important benefit is the revenue it generates. Publishers can broaden their selection of SSPs (Supply Side Platforms) as the fill rate and impression allocation improve. With more control over it, publishers can pick which bidders are allowed to participate in their auctions and even favor advertisers in their auctions.
Advertisers have an equal chance to bid on ad space in the publisher’s inventory. Advertisers have the same opportunity to bid in the auction as everyone else, and the highest bidder receives the ad slot.
Read our article on Programmatic Advertising and Real-Time Bidding
Setting up a Header bid
The Ad Manager, header bidding wrapper, and SSP adapters must all be connected in order to configure. The wrapper is a Javascript tag that serves as a container for all of the code that controls bidders and programmatic auctions.
Several demand partners’ codes are used to determine the auction’s protocols. Once the code is added to the publisher’s website, the wrapper receives the SSP bids and selects one bidder for the ad spot. If the process takes too long, wrappers provide a timeout functionality that will send a timeout response. This ensures that the user does not have to wait for your ad.
Source: Google
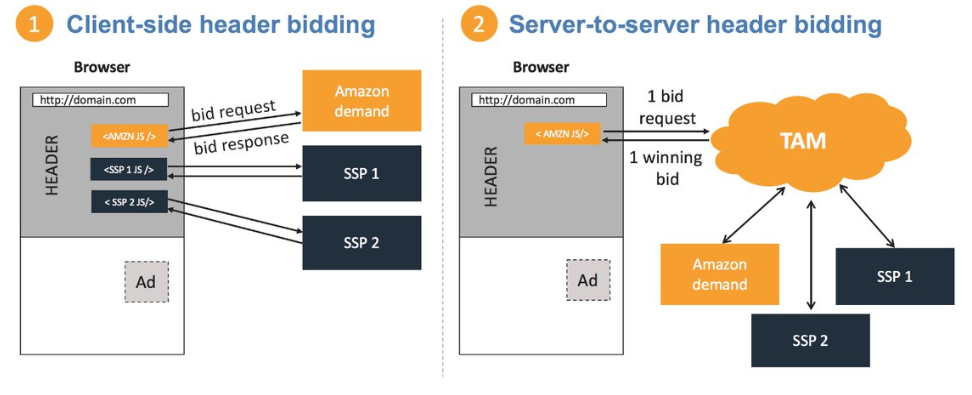
Client-Side vs Server-Side Header Bidding
Client-Side Header Bidding
When numerous advertisers connect directly to the header bidder wrapper, a significant amount of JavaScript is run on the page, boosting the responsiveness of the website and ad load times. The publishers must do this by adding a piece of code to their website. This code runs when a page loads and sends an ad request to a number of demand partners. The highest bidder wins the auction and has their ad served once their demand partners submit bids. By hosting the auction process on a cloud-based external server, Google’s AdX eliminates the lag. The ad server subsequently distributes the advertisements to all pertinent SSPs.
Server-Side Header Bidding
Similar to server-side header bidding, client-side header bidding transmits bids through a central browser as opposed to the user’s browser. This provides advantages to publishers and saves a significant amount of time in the process.
We provide header bidding to our publishers via eReleGo’s proprietary pre-bid adapter, “eRGADX”. Click here to explore. We comply with privacy requirements such as GDPR, CCPA, and COPPA with ad formats like display, video, and native.
